Week of 28 September 2021
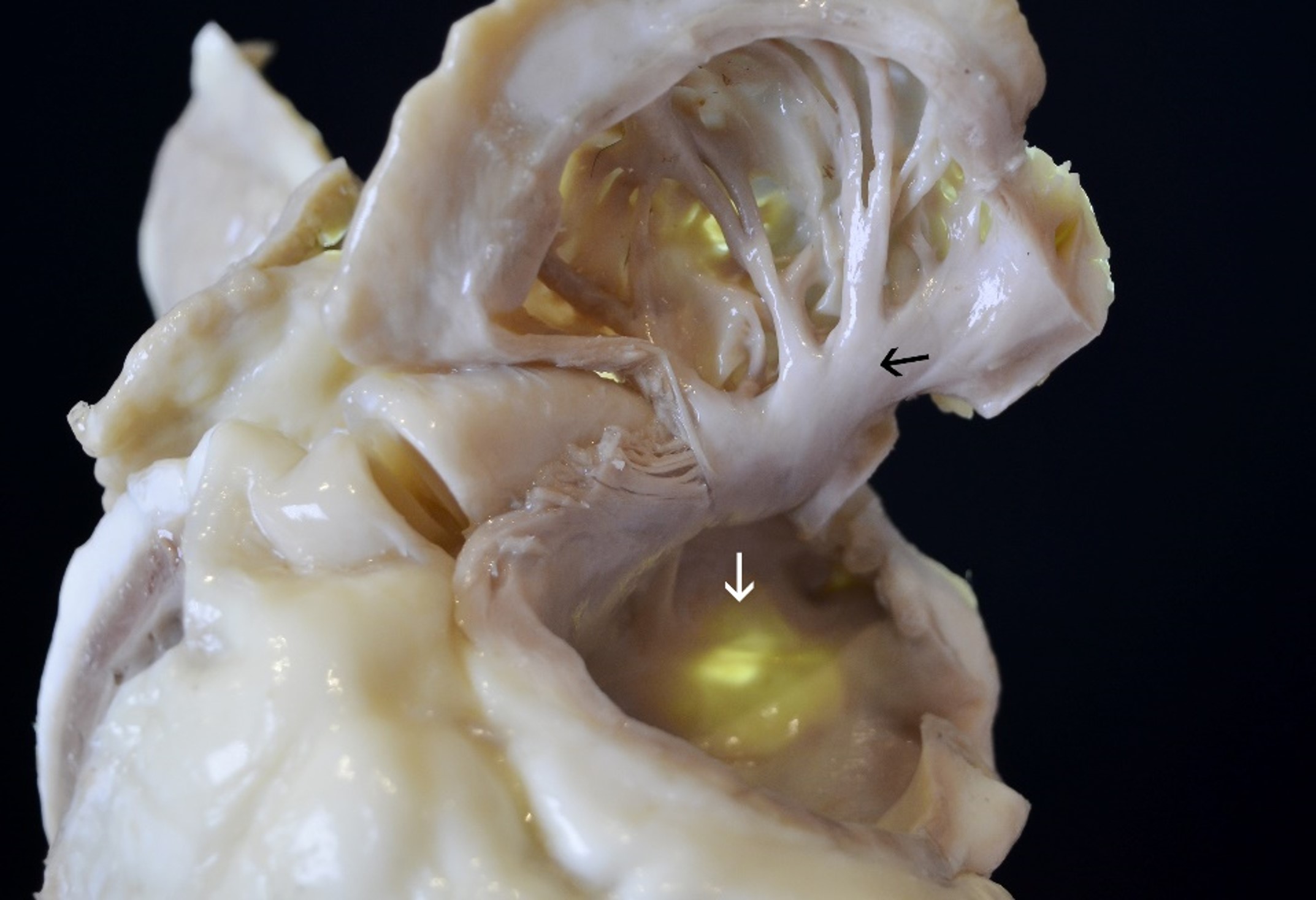
The fossa ovalis (as seen from the left side of the heart)!
The fossa ovalis is the small oval depression in the interatrial septum at the site of the closed foramen ovalis, which closes once fetal circulation ceases in the first few minutes of postnatal life. It represents the overlapping primary and secondary septa of the interatrial septum. It has a semilunar depression inferiorly which is the floor of the fossa, and the adjacent ridge is at the superior margin of the fossa. Of note, the superior−anterior portion of the fossa ovalis is typically targeted for transseptal puncture access from a superior approach.
White arrow: Fossa ovalis
Black arrow: Left atrial roof
Plastination is a technique used to preserve organs and tissues in which the water and fat are replaced by plastic materials, yielding specimens that do not decay and retain most properties of the original sample.
This plastinated heart is one example from the comprehensive suite of Surgical Training and Pathology Services offered by IMMR’s in-house team of veterinary cardiac surgical specialists and Board-certified Veterinary Pathologists, in collaboration with the veterinary school of Maisons-Alfort, Paris.
Contact us to learn more and discuss your preclinical research and pathology needs.
Follow us on LinkedIn and don’t miss new images from our library that we post every Tuesday, when you’ll have another chance to recognize, identify or diagnose what is shown. You can also stay updated on some of the latest developments in Preclinical Science. Stay tuned!


